Fuchsia Plant: How to Grow and Care for Fuchsia Flowers
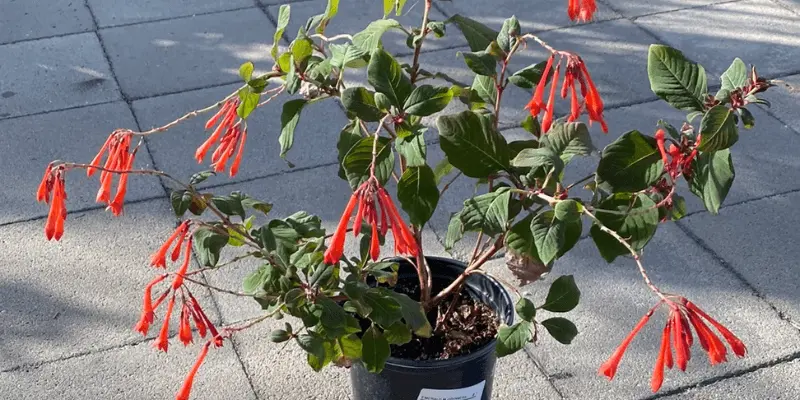

The Fuchsia plant, scientifically known as Fuchsia spp., is a captivating and ornamental shrub native to Central and South America. It is renowned for its distinctive pendulous flowers, which come in a wide array of striking colors, including shades of red, pink, purple, and white. Fuchsia plants have a unique and elegant appearance, making them a popular choice among gardeners and flower enthusiasts. Fuchsia flowers are renowned for their vibrant colors and graceful appearance. Growing and caring for these stunning plants can be a rewarding experience for any gardener.
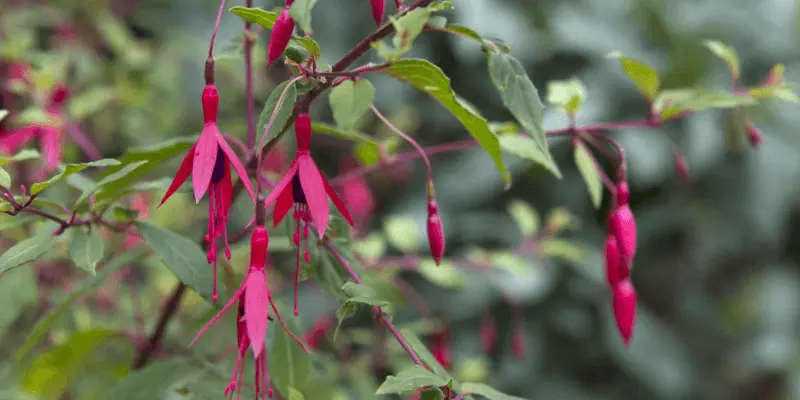

Appearance:
- Fuchsia plants typically grow as shrubs or small trees, ranging in height from 12 inches to 10 feet, depending on the variety.
- The leaves of Fuchsia plants are often dark green and can have a glossy or matte texture.
- The most striking feature of the Fuchsia plant is its tubular, pendulous flowers, which hang gracefully from the branches and have a distinct, lantern-like shape.
- Fuchsia flowers exhibit a captivating color combination, with the outer petals often being a different shade than the inner ones. This creates a stunning contrast that adds to their visual appeal.
Varieties:
There is a wide variety of Fuchsia species and cultivars available, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are some popular varieties of Fuchsia plants:
Fuchsia magellanica: This is one of the most common and hardy species of Fuchsia. It is known for its upright growth habit and delicate, pendulous flowers that typically come in shades of red and pink. Varieties of Fuchsia magellanica include “Riccartonii” with deep red flowers and “Aurea” with golden-yellow foliage.
Fuchsia triphylla: Also known as the “Firecracker Fuchsia,” this variety stands out for its fiery red, tubular flowers and dark green, lance-shaped leaves. It tends to have an upright, bushy growth habit and is a favorite among hummingbirds.
Fuchsia hybrida: Hybrid Fuchsia plants have been bred for their diverse flower colors and forms. They often feature double or semi-double blooms and come in a wide range of colors, including white, purple, and various shades of pink and red. Some popular hybrid varieties include “Swingtime,” “Gartenmeister Bonstedt,” and “Dollar Princess.”
Fuchsia boliviana: This species is recognized for its elegant, long, and tubular flowers, which are usually bright red or orange-red. It has a more upright and tree-like growth habit compared to other fuchsias.
Fuchsia procumbens: Unlike the typical pendulous fuchsia, this variety is known for its trailing and creeping growth habit. It produces small, greenish-yellow flowers and is often grown as a ground cover.
Fuchsia regia: Also referred to as the “Royal Fuchsia,” this variety features large, single, and vibrant purple-red flowers. It can grow as a small tree and is prized for its regal appearance.
Fuchsia splendens: This species is valued for its elegant, pendulous flowers, which can be crimson or pink. It is characterized by its semi-trailing growth habit.
Fuchsia arborescens: Known as the “Lilac Fuchsia,” this variety produces clusters of lilac-pink flowers and has a shrubby growth habit. It is native to Central America.
Growing Conditions:
- Fuchsia plants thrive in partial shade, making them ideal for gardens with dappled sunlight or filtered light. They prefer protection from intense afternoon sun and strong winds.
- The soil should be well-draining and rich in organic matter. Fuchsia plants tend to thrive in slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 6 and 6.5.
How to Grow Fuchsia Plant

- Fuchsia plants come in various species and cultivars, each with its own unique characteristics. Before you start, research and select the fuchsia variety that suits your climate and preferences. Some varieties are hardy, while others are more delicate.
- This plants thrive in partial shade, which means they should receive filtered sunlight or morning sun and be protected from harsh afternoon rays. Ensure the location you choose provides these conditions.
- Fuchsias prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. You can amend your garden soil with compost to improve its texture and fertility. Aim for slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 6 and 6.5.
- plants can be grown from seed, but it’s easier for beginners to start with established seedlings or cuttings. Plant your fuchsia at the same depth it was in its nursery pot, and space multiple plants adequately to allow for growth.
Watering: This plants like consistent moisture, but they don’t tolerate waterlogged soil. Water your fuchsias regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist. It’s best to water at the base of the plant to avoid wetting the foliage, which can lead to disease.
Mulching: Apply a layer of mulch around the base of your plants to help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain a more consistent soil temperature. Organic mulches like straw or compost work well.
Fertilize: Fuchsias benefit from regular feeding during the growing season. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer designed for flowering plants. Follow the recommended application rates on the fertilizer label.
Pruning and Deadheading: To encourage bushy growth and continuous blooming, prune your plants regularly. Pinch off spent flowers (deadhead) to redirect the plant’s energy into producing new blooms.
Fuchsia plant care from Pests and Diseases:
Keep an eye out for common pests like aphids and whiteflies. Treat any infestations promptly with appropriate pesticides or insecticidal soap. Also, watch for signs of diseases like rust or powdery mildew and take action if necessary.

Winter Care:
In areas with cold winters, consider bringing your fuchsia plants indoors or into a greenhouse to protect them from frost. Prune them back in late fall to remove dead growth and reduce the risk of disease. With proper care and attention, your fuchsia plant will reward you with an abundance of vibrant, pendulous flowers that will add charm and elegance to your garden or patio. Enjoy the beauty of these unique blooms as they flourish and thrive in their ideal conditions.
Common Diseases Affecting Fuchsia Plants
Gray Mold (Botrytis cinerea):
Gray mold is a fungal disease that often affects this plants, especially in humid conditions. It appears as grayish, fuzzy mold on leaves, stems, and flowers.
Treatment:
- Remove affected plant parts promptly to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Improve air circulation around the plant.
- Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can promote mold growth.
- Apply a fungicide specifically designed to combat gray mold, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
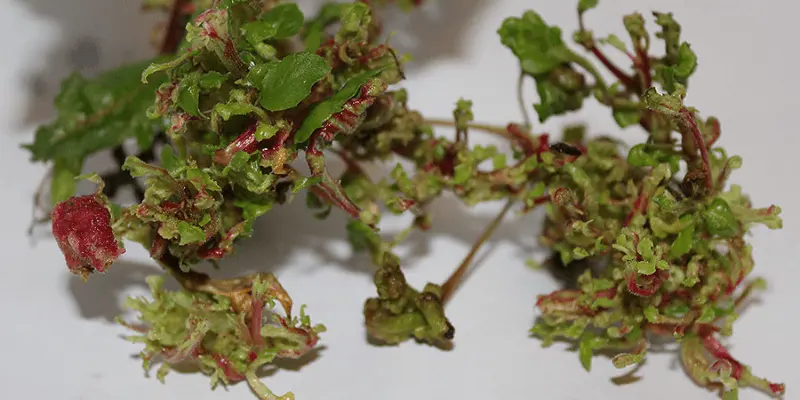

Powdery Mildew (Erysiphe spp.):
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that manifests as a white, powdery substance on the leaves and stems of the plant.
Treatment:
- Prune affected parts and dispose of them.
- Ensure adequate spacing between plants to improve air circulation.
- Apply a fungicide labeled for powdery mildew control.
- Water the plant at the base to keep the foliage dry.
Rust (Puccinia spp.):
Rust is another fungal disease that affects Fuchsia plants. It presents as small, orange or rust-colored spots on the leaves.
Treatment:
- Remove and destroy infected leaves.
- Avoid overhead watering and keep the foliage dry.
- Apply a fungicide suitable for rust control as directed by the product label.
Preventative Measures:
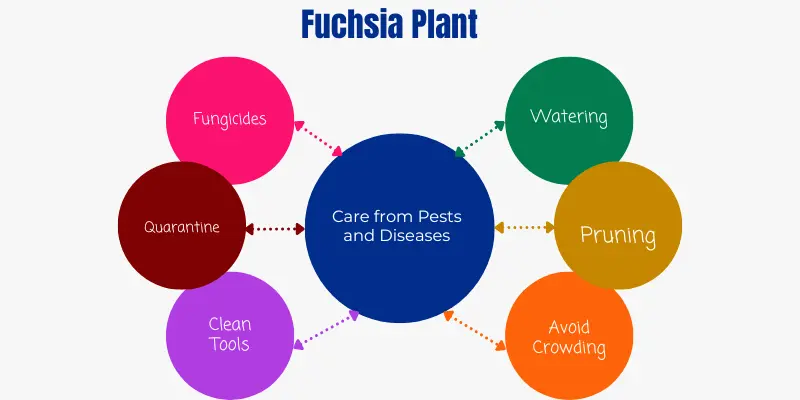
Proper Spacing: Ensure your plants are adequately spaced to allow for good air circulation. This helps prevent the buildup of humidity around the plants, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Watering: Water your plants at the base rather than overhead to keep the foliage dry. This reduces the chance of fungal spores finding a conducive environment to grow.
Pruning: Regularly prune your plant to remove dead or diseased branches and spent flowers. This helps improve air circulation and reduces the spread of diseases.
Avoid Crowding: Avoid overcrowding your plants with other vegetation. Crowded conditions can increase humidity and make it easier for diseases to spread.
Fungicides: Consider using fungicides as a preventative measure during the growing season, especially if you have a history of fungal issues with your Fuchsia plants.
Quarantine: If you introduce new plants to your garden, quarantine them for a period to ensure they are disease-free before placing them near your Fuchsia plants.
Clean Tools: Use clean and disinfected pruning tools to avoid transferring diseases from one plant to another.
By following these preventative measures and promptly addressing any disease issues, you can help keep your Fuchsia plants healthy and thriving. Regular monitoring and care will go a long way in preventing and managing disease attacks on your beloved Fuchsia plant.


